
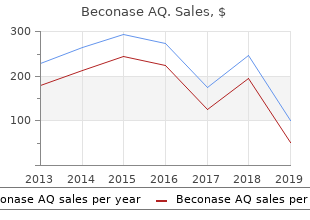
By: Brian M. Hodges, PharmD, BCPS, BCNSP

https://directory.hsc.wvu.edu/Profile/38443
There is a robust relation with early organ dysfunction and mortality in these sufferers allergy testing geelong buy beconase aq australia, which makes intra-belly hypertension a beautiful target for intervention allergy shots heart palpitations order beconase aq canada. Several reports conclude that this phenomenon occurs within the first 5 days after admission allergy treatment sugar buy cheap beconase aq, and that the kinetics of inta-belly hypertension is important: sufferers with persistent intra-belly hypertension seem to allergy symptoms neck pain cheap generic beconase aq canada be at the highest risk for mortality. Several strategies to reduce intra-belly pressure have been developed, and given the pathophysiology, percutaneous drainage of ascites is a first logical step. However, if conservative measures fail to reduce intra-belly pressure in a setting with ongoing or worsening organ dysfunction, belly decompression is really helpful. Intra-belly hypertension and intra-belly compartment syndrome have been described most frequently in sufferers with belly trauma or after emergency belly surgical procedures similar to aortic aneurysm restore (De Waele, 2008). The intra-belly hypertension is defined as a sustained or repeated pathologic elevation of the intraabdominal pressure above 12mm Hg. The intra-belly compartment syndrome is described as the sustained elevation of intra-belly pressure above 20mmHg in combination with newly developed organ dysfunction (Malbrain et al. It was shown that intra-belly hypertension is related to higher mortality and morbidity charges, and prolonged intensive care unit stay, compared to different sufferers who had regular intra-belly pressure (Sugrue et al. Intra-belly hypertension has been recognized as a reason for organ dysfunction in critically unwell sufferers, together with those 242 Acute Pancreatitis suffering from extreme acute pancreatitis (Balogh et al. Placement of a urinary catheter for the monitoring of intra-belly pressure can be essential within the extreme acute pancreatitis sufferers. Hemodynamic instability requiring vasoactive drugs, acute renal failure and respiratory failure are the most obvious clinical signs and signs which have been related to intra-belly hypertension. The affiliation between intra-belly hypertension and growth of organ dysfunction in extreme acute pancreatitis is properly documented. Therefore, intra-belly pressure should be measured routinely in sufferers admitted to the intensive care unit with extreme acute pancreatitis, and intra belly pressure should be considered a target for intervention in all sufferers. Decompressive laparotomy has been shown to successfully reduce intra-belly pressure and reverse the signs typically related to belly compartment syndrome (De Waelle et al. In selected sufferers with intensive retroperitoneal fluid collections, a lumbotomy might provide entry to the retroperitoneal area, and permit evacuation of pancreatic necrosis as properly. The management of the open abdomen following decompression in extreme acute pancreatitis is challenging. The greatest presently out there technique is the utilization of the vacuum-assisted closure technique aiming for gradual closure of the belly wall. The use of a vacuum assisted closure system ensures an ideal seal of the peritoneal cavity, avoiding potential superinfection of the pancreatic or peripancreatic necrosis. Intra-belly hypertension seems to have a significant role in contributing to the early multi organ dysfunction syndrome, subsequent issues and mortality in extreme acute pancreatitis. Intra-belly pressure monitoring is obligatory for all sufferers who develop organ dysfunction, and intra-belly pressure should be a target for intervention when intra-belly hypertension and organ dysfunction persist. Surgical decompression should be considered in all sufferers with persistent organ dysfunction after three days or later (Sugrue et al. Clinical group of sufferers and the strategies All sufferers who have been hospitalized as a result of the acute pancreatitis signs within the period from January 2003 until December 2008 at the First Department of Surgery, University Hospital, in Kosice, have been included to this examine. Those sufferers, who have been primarily hospitalized and treated at different workplaces and have been moved to our institute throughout their illness, have been excluded from this examine. The whole number of the sufferers with acute pancreatitis throughout onset signs was 258 ones. All sufferers have been hospitalized at the Intensive Care Unit, they acquired the usual intensive care (palliation of ache, nasal gastric tube, central vein catheter, urinary bladder catheter, intensive monitoring of the fundamental important functions, intensive rehydratation treatment, Changes within the Management of Treatment in Acute Pancreatitis Patients 243 giving the inhibitors of proton pump, low molecular weight heparin, giving the prophylactic antibiotic therapy). In the case of biliary acute pancreatitis, primarily joined with jaundice, cholangitis or ultrasound suspicion for the presence of the stones in common bile duct, the sufferers have been underwent urgent endoscopic retrograde cholangio pancreatography in the course of the first 48 hours after onset acute pancreatitis. The first computer tomography examination was carried out first time after 48 hours from the beginning of illness. The prognosis of the contaminated necrosis we did in accordance with the clinical finding, inflammatory markers (white blood cells, C-reactive protein, procalcitonin), and ultrasound and computer tomography finding (presence of gasoline bubbles). Patients with multi organ failure have been moved from the Intensive Care Unit to be hospitalized at the Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Medicine of our institute. The second Group B included the sufferers hospitalized from January 2006 until December 2008. This group was studied prospectively, in accordance with the clinical protocol ready in advance, which mirrored the adjustments in management of the sufferers with the extreme acute pancreatitis after confirmation of necrosis. Enteral diet was utilized if no signs of the cardiovascular instability have been present. We used the enteral diet enriched of the glutamine, arginine and omega-three fatty acids and fibres. The dose was gradually elevated from 20ml/hour to 80ml/hour (most 1000ml/24 hours). The second change consists of an utility of the epidural catheter to palliate the ache and to restoration of intestinal peristaltic. The continual measurement of the intra-belly pressure with the catheter in urinary bladder was used. Necrosectomy was indicated and carried out as late as potential; normally the surgical procedure was pushed to the third or fourth week of hospitalization. It follows less frequency in Group A, nonetheless the male/feminine ratio and incidence of the extreme acute pancreatitis was similar. The share of the sufferers with necrotic pancreas and the 244 Acute Pancreatitis sufferers, who wanted endoscopic retrograde cholangiography procedure, was similar as properly. Group A Group B Number of sufferers ninety seven 161 Male/Female 53 : 44 ninety : seventy one Mild acute pancreatitis eighty four (86%) 132 (eighty two%) Severe acute pancreatitis thirteen (14%) 29 (18%) Number of sufferers + endoscopic retrograde 34 (35%) 53 (33%) cholangiopancreatography Table 1. Groups of sufferers suffered from acute pancreatitis, group A (2003-2005), group B (2006-2008). Further we will be involved solely with the sufferers with extreme acute pancreatitis. More detailed attribute of sufferers with extreme acute pancreatitis is documented in table 2. Group A Group B Number of sufferers thirteen 29 Male/Female eight/5 16/thirteen Mean of age 38,5 year forty two year Etiology of acute pancreatitis Alcohol 7 (fifty four%) 14 (48%) Biliary illness 5 12 Other 1 three Ranson score three,9 (three-9) 4,0 (2-9) Number of sufferers with computer tomography scan necrosis greater than 30% 12 (ninety two%) 26 (ninety%) Patients hospitalized at the Department of Anesthesiology et Intensive Medicine 6 (46%) eleven (37%) Table 2. Group of sufferers suffered from extreme acute pancreatitis More detailed description of group of sufferers with extreme acute pancreatitis is documented in table 2. Also we noticed the upper number of sufferers, who wanted hospitalization at the Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Medicine. During the hospitalization, primarily in the course of the period from seventy two hours to 7th day, we supplied intensive treatment in both group of sufferers, nonetheless in some instances despite our intensive effort, the multi organ failure occurred. In the case of presence of belly compartment syndrome, we indicated the surgical intervention together with intra belly decompression. Presence of the contaminated pancreatic necrosis or abscess was a clear indication for surgical intervention. Changes within the Management of Treatment in Acute Pancreatitis Patients 245 Sterile necrosis + Infected Abscess Together Mortality multi organ necrosis failure Time A B A B A B A B A B Till seventy two hours 1 1 1 1 1 1 Till 7 days three 2 three 2 three 1 After 7 days 1 1 1 1 After 14 days 1 three 1 three 1 1 After 21 days 1 4 1 1 5 Together 4 4 three 7 1 7 12 5 three seventy one% 25% Table three. Comparing Group B, primarily within the case of contaminated necrosis, the surgical operations have been pushed to the third or fourth week. This was mirrored additionally within the mortality of operated sufferers, after we recorded seventy one% mortality in Group A and 25% of mortality in Group B. While in the course of the first days we carried out solely the surgical revision and drainage, or open abdomen. In the case of contaminated necrosis we carried out necrosectomy with closed continuous lavage. There are additionally documented the number of sufferers with reoperations in both groups of sufferers, which is less frequent in Group B. Primary surgery Repeated surgery Mortality Type of surgery A B A B A B Revision, drainage, open 2 1 0 0 2 0 abdomen, jejunostomy Revision, drainage, 1 4 1 0 0 three jejunostomy Necrosectomy, 4 7 2 4 three 0 continuous lavage Together 7 12 three (43%) 4 (33%) 5 three Table 4. Type of surgical procedures and mortality of sufferers in group of sufferers A and B. Six sufferers have been found with non contaminated necrosis 46% in Group A (2003 2005), however seventeen sufferers have been documented with non contaminated necrosis 58% in Group B (2006-2008). There was statistically vital lower in mortality in group of sufferers B (p=0. While solely 2 affected person�s useless for the pancreatic sepsis with multi organ failure, the remainder 10 affected person�s useless for multi organ failure in first days after the admitting to hospital. Group of sufferers A Group of sufferers B (2003-2005) (2006-2008) P Number of sufferers thirteen 29 Death 7 (fifty four%) 5 (18%) 0.
Asymmetric refractive error can result in allergy forecast charlottesville va order beconase aq in india (anisometropic) amblyopia allergy medicine fruit juice generic beconase aq 200MDI visa, which is detected solely by assessing visual acuity allergy forecast park city utah order beconase aq now. Anterior & Posterior Segment Examination Further examination needs to allergy shots salt lake city order beconase aq uk be tailored to every youngster�s age and talent to cooperate. It is mostly simpler in neonates and babies than in young children because they are often restrained simply by being wrapped in a blanket, and examination is often simply achieved by allowing the infant to feed or nurse in the course of the examination. Anterior section examination within the young youngster may depend on the use of hand mild and loupe, however slitlamp examination is often attainable in babies with the cooperation of the mother and in young children with appropriate encouragement. Measurement of intraocular pressure and gonioscopy incessantly necessitate examination under anesthesia. The macula has a brilliant �mother-of-pearl� appearance with a suggestion of elevation, which is extra pronounced in heavily pigmented infants. At three�4 months of age, the macula becomes barely concave and the foveal mild reflection appears. The peripheral 807 fundus within the infant is grey, in contrast to the orange-pink fundus of the adult. In extra heavily pigmented infants, a grey-blue sheen is seen throughout the periphery. During the following a number of months, pigment continues to be deposited within the retina, and normally at about 2 years of age, the adult shade is clear. Congenital Abnormalities of the Globe Failure of formation of the optic vesicle results in anophthalmos. Failure of optic vesicle/fissure closure produces colobomas of the iris, retina, and/or choroid. Abnormally small eyes can be divided into nanophthalmos, by which perform is regular, and microphthalmos, by which perform is irregular and there could also be different ocular abnormalities similar to cataract, coloboma, or congenital cyst. Lid Abnormalities Congenital ptosis is often due to dystrophy of the levator muscle of the upper lid (see Chapter 4). Severe ptosis can result in unilateral astigmatism or visual deprivation, and thus cause amblyopia. Palpebral coloboma is a cleft of both the upper or decrease eyelid due to incomplete fusion of fetal maxillary processes. Congenital eyelid colobomas are commonly seen in association with craniofacial disorders similar to Goldenhar�s syndrome. Megalocornea is an enlarged cornea with regular clarity and function, normally transmitted as an X-linked recessive trait and an isolated anomaly. Iris & Pupillary Defects Displacement of the pupil (corectopia) is normally upward and outward. Coloboma of the iris signifies incomplete closure of the fetal ocular cleft and normally happens inferiorly and nasally. It could also be related to coloboma of the lens, choroid, and optic nerve, and involvement of those constructions can be related to profound discount of vision. Aniridia (absence of the iris) is a rare abnormality, incessantly related to secondary glaucoma (see Chapter 11) and normally due to an autosomal dominant hereditary pattern. There is a significant association with Wilms� tumor for which the danger can be decided by genetic testing, thus identifying the children who must undergo screening by renal ultrasound each three months until age eight. Abnormalities in shade include albinism, due to the absence of regular pigmentation of the ocular constructions and incessantly related to poor visual acuity and nystagmus; and heterochromia, which is a difference in shade within the two eyes that could be a main developmental defect with no useful loss, due to congenital Horner�s syndrome or secondary to an inflammatory process. Lens Abnormalities the lens abnormalities most incessantly noted are cataracts (see Chapter eight). Maternal rubella in the course of the first trimester of being pregnant is a typical cause in emerging international locations. Other congenital cataracts have a hereditary background, with autosomal dominant transmission being the commonest in developed international locations. The innermost fetal nucleus of the lens varieties early in embryonic life and is surrounded by the embryonic nucleus. If a congenital cataract is just too small to occlude the pupil, sufficient visual acuity is attained by viewing around it. Good visual outcomes have been reported with each unilateral and bilateral cataracts handled by early surgical procedure with prompt correction of aphakia and amblyopia remedy. Aphakic correction is completed by using extended-wear contact lenses with the power modified incessantly to keep optimal correction as the globe grows and the refractive standing adjustments or by implantation of an intraocular lens, however determining the suitable energy is troublesome. Whether this may be dealt with adequately is the major determinant in deciding whether or not early surgical procedure for monocular congenital cataract is justified. In the case of bilateral congenital cataracts, the time interval between operating on the 2 eyes have to be as short as attainable if amblyopia within the second eye is to be avoided. Developmental Anomalies of the Anterior Segment Failure of migration or subsequent development of neural crest cells produces abnormalities involving the anterior chamber angle, iris, cornea, and lens. Glaucoma is a significant scientific drawback that often requires surgical intervention, nearly as good management 810 of intraocular pressure is required earlier than contemplating corneal transplantation. Congenital Glaucoma Congenital glaucoma (see Chapter 11) may occur alone or in association with many different congenital lesions. Early diagnosis and remedy are important to protect helpful vision and stop permanent blindness. Early signs are corneal haze or opacity, elevated corneal diameter, and elevated intraocular pressure. The major differential diagnoses are forceps injuries at start, developmental anomalies of the cornea or anterior section, and mucopolysaccharidoses similar to Hurler�s syndrome, of which none produce enlargement of the globe. Vitreous Abnormalities In premature infants, remnants of the tunica vasculosa lentis are incessantly visible, in front of and/or behind the lens. At different occasions, remnants of the primitive hyaloid system fail to absorb completely, leaving both a cone on the optic disk that tasks into the vitreous (Bergmeister�s papilla) or a gliotic tuft on the posterior lens capsule (Mittendorf�s dot). Persistent hyperplastic main vitreous is a crucial reason for leukocoria that have to be differentiated from retinoblastoma, congenital cataract, and retinopathy of prematurity. Posterior polar chorioretinal scarring is a feature of toxoplasmosis and different maternally acquired intrauterine infections. They are normally benign, similar to minor abnormalities of the retinal vessels on the nerve head and tilted disks due to an oblique entrance of the nerve into the globe, however they might be related to severe visual loss within the case of optic nerve hypoplasia or the rare central coloboma of the disk (morning glory syndrome) (see Chapter 14). Optic nerve hypoplasia is a nonprogressive congenital abnormality of 1 or each optic nerves by which the variety of axons within the involved nerve is lowered. The degree of visual impairment varies from regular acuity with all kinds of visual area defects to no perception of sunshine. Clinical diagnosis is hampered by the difficulties of examining young children and the subtlety of the scientific signs. In extra marked instances, the optic disk is clearly small and the circumpapillary halo of the normal-sized scleral canal produces the characteristic �double ring signal. Optic nerve hypoplasia is incessantly related to midline deformities, together with absence of the septum pellucidum, agenesis of the corpus callosum, dysplasia of the third ventricle, pituitary and hypothalamic dysfunction, and midline facial abnormalities. Jaundice and hypoglycemia within the neonatal period and progress retardation, hypothyroidism, and diabetes insipidus during childhood are necessary consequences. More severe intracranial abnormalities similar to anencephaly and porencephaly additionally occur. Endocrine and neuroradiographic investigations must be undertaken in all sufferers with optic nerve hypoplasia. Visual performance in children with optic nerve hypoplasia sometimes could also be improved by occlusion remedy. Extraocular Dermoids Congenital rests of floor ectodermal tissues may result in formation of dermoids that occur incessantly within the extraocular constructions. They occur most commonly superolaterally, arising from the frontozygomatic suture. Approximately 6% have extra prolonged signs, of which the majority will also resolve aided by lacrimal sac massage and remedy of episodes of conjunctivitis with topical antibiotics. Nasolacrimal probing is normally curative within the remainder and is best deferred until about 1 year of age. In a couple of instances, short-term intubation and/or balloon catheter dilation of the lacrimal system or lacrimal surgical procedure is required. The risk of extra in depth congenital nasolacrimal anomalies must be borne in thoughts in sufferers with craniofacial anomalies. Epiphora may be due to inflammatory anterior section illness, lid abnormalities, and congenital glaucoma.
Chylomicronemia and the chylomicronemia syndrome: a practical strategy to allergy testing east meadow beconase aq 200MDI discount administration allergy symptoms ear pressure order beconase aq us. Safe and speedy resolution of severe hypertriglyceridaemia in two patients with intravenous insulin allergy shots nz buy generic beconase aq 200MDI on-line. A novel advanced deletion-insertion mutation mediated by Alu repetitive components results in allergy symptoms after swimming generic 200MDI beconase aq fast delivery lipoprotein lipase deficiency. Dyslipidaemia in a boy with recurrent stomach pain, hypersalivation and decreased lipoprotein lipase exercise. A case of acute pancreatitis with hyperlipemia and hyperglycemia induced by alcohol abuse. Insulin infusion to treat severe hypertriglyceridemia associated with pegaspargase therapy: a case report. Insulin acutely inhibits intestinal lipoprotein secretion in people in part by suppressing plasma free fatty acids. Fatty acid esters of steroids: synthesis and metabolism in lipoproteins and adipose tissue. Severe hypertriglyceridemia in diabetic ketoacidosis accompanied by acute pancreatitis: case report. Hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis-treatment with heparin and insulin. Heparin and insulin within the treatment of hypertriglyceridemia-induced severe acute pancreatitis. Biphasic effects of low-molecular weight and conventional heparins on chylomicron clearance in rats. Lower plasma levels of lipoprotein lipase after infusion of low molecular weight heparin than after administration of standard heparin point out more speedy catabolism of the enzyme. Decreasing the plasma triglyceride degree in hypertriglyceridemia induced pancreatitis in pregnancy: a case report. Pancreatitis could occur with a traditional amylase concentration in hypertriglyceridaemia. Opportunities in somatostatin analysis: biological, chemical and therapeutic aspects. Hypertriglyceride Induced Acute Pancreatitis 277 [142] Taniyama Y, Suzuki T, Mikami Y, Moriya T, Satomi S, Sasano H. Systemic distribution of somatostatin receptor subtypes in human: an immunohistochemical study. Somatostatin type 2A receptor immunoreactivity in human pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Microinjection of exogenous somatostatin within the dorsal vagal advanced inhibits pancreatic secretion via somatostatin receptor-2 in rats. Changes in somatostatin receptor expression of the pancreas and effectiveness of octreotide in rats with acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Characterization of somatostatin receptor subtype-specific regulation of insulin and glucagon secretion: an in vitro study on isolated human pancreatic islets. Hypertriglyceridemic acute pancreatitis throughout pregnancy: prevention with food regimen therapy and omega-3 fatty acids within the following pregnancy. Prescription omega-3 fatty acid as an adjunct to fenofibrate therapy in hypertriglyceridemic subjects. Therapeutic plasma trade in patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia: a multicenter study. Guidelines on using therapeutic apheresis in medical apply: evidence-based mostly strategy from the Apheresis Applications Committee of the American Society for Apheresis. Dietary medium-chain triacylglycerol prevents the postprandial rise of plasma triacylglycerols but induces hypercholesterolemia in major hypertriglyceridemic subjects. High-monounsaturated fatty acid diets lower each plasma ldl cholesterol and triacylglycerol concentrations. Effect of fibrates on lipid profiles and cardiovascular outcomes: a systematic evaluate. Relapsing acute pancreatitis induced by re-publicity to the ldl cholesterol lowering agent bezafibrate. Efficacy and security of rosuvastatin and fenofibric acid mixture therapy versus simvastatin monotherapy in patients with hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia: a randomized, double-blind study. Triglycerides and atherogenic dyslipidaemia: extending treatment beyond statins within the high-threat cardiovascular patient. Effects of prescription omega-3-acid ethyl esters on non-high-density lipoprotein ldl cholesterol when coadministered with escalating doses of atorvastatin. Role of n-3 fatty acids within the treatment of hypertriglyceridemia and cardiovascular disease. Dose-response effects of omega-3 fatty acids on triglycerides, inflammation, and endothelial operate in wholesome individuals with average hypertriglyceridemia. In many instances, these anatomic entities could be succesfully treated with radiological interventional methods. It is troublesome to correctly interpret the articles that evaluate the treatment of quite a few patients as a result of the nomenclature is unclear. Not not often, it spreads into the chest, mediastinum and/or into the pararenal area. The rich pancreatic enzyme content material of the fluid can point out communication with the pancreatic duct or point out parenchymal necrosis. In a major variety of instances (about 30-50%), spontaneous resolution occurs with out surgical or different intervention. The most frequent complaints caused by a big, 8-15 cm measurement acute fluid assortment are pain, pressure, and increasing stomach stress which can significantly worsen the efficiency of respiration [1,9]. The variety of acute fluid collections correlate to the severity of the pancreatitis, the size of hospitalization and mortality [19]. In a small sized fluid assortment, conservative treatment (naso-jejunal feeding, the resting of pancreas) is normally efficient. With the development of interventional radiology and manipulative laparo-endoscopy there are different possibilities to evacuate these fluid collections with out operation [1,6,11,14,21,25,35,40,44]. For the treatment of sterile fluid assortment percutaneous puncture and drainage are widely utilized. It is disputed whether repeated punctures or drainage is probably the most suitable for the treatment of fluid collections. However, that is succesful only in a number of instances and drainage or surgical intervention follows [6,28,40,44]. According to those that are professional drainage within the treatment of sterile acute peripancreatic fluid collections, drainage could be utilized effectively [1,3,four,14,21,25,34,35,40,44]. According to the literature the speed of iatrogenous infection is about 8-27% [12,25,28,40]. Surgery can often be prevented by drainage treatment, and in different instances the intervention is suitable for delaying operative treatment. These instances are equivalent to the pathological entity accepted within the modified Atlanta Classification as postnecrotic peripancreatic/pancreatic fluid assortment and walled off pancreatic necrosis. According to different authors the evacuation of necrosis and fluid assortment is feasible with the help of irrigation by way of 14-30 F bore drains. For such treatment more catheters ought to be placed within the cavity [5,10,11,12,18,21,26,29,33,36,38,43]. With so-referred to as �sinus tract endoscopy� necrectomy could be carried out effectively following the dilatation of the drain�s channel [23,36,43]. More than 20% of the patients treated with the minimal invasive methodology recovered with out operation. Necrosectomy throughout operation is the acceptable methodology in instances of unsuccessfully treated patients [3,6,10,11,12,22,24,26,28, 33,34,36,43]. It develops most regularly within the surroundings of the pancreas but mediastinal or pelvic appearances are additionally recognized. About four weeks are wanted for the development of the mutation from the beginning of the illness. Its content material is normally sterile but generally bacteria could be detected without any medical manifestation, in different instances it incorporates pus [5]. In its cavity pseudoaneurysm can develop which can trigger deadly bleeding [2,6,11,14,28,33,37].
Purchase 200MDI beconase aq with mastercard. Pollen Allergy Season 4 EP07.
Percussion can also be carried out over an enlarged spleen allergy testing dairy purchase 200MDI beconase aq, bladder and different plenty as well allergy shots how often safe beconase aq 200MDI. In a girl with a large ovarian cyst percussion reveals resonance in the flanks and dullness in the midline whereas abdominal distention as a result of allergy forecast bryan tx purchase beconase aq uk intestinal obstruction results in allergy medicine 2013 buy discount beconase aq online hypertympanicity all over the abdomen. Auscultation the stethoscope must be positioned on one web site on the abdominal wall, ideally on the best decrease quadrant, to hear for bowel sounds, and kept there until sounds are heard. In simple, acute mechanical obstruction, bowel sounds are extreme and exaggerated. In generalized peritonitis, bowel exercise rapidly disappears and a state of paralytic ileus ensues and the abdomen shall be silent. Vascular bruits could also be heard over the aorta, iliac arteries, renal arteries and the femoral arteries. A bruit can also be heard over a hepatoma due to elevated flow with in the tumor. The Anus and Rectum: the left lateral position is finest for routine examination of the rectum. The examiner places on a disposable pair of gloves, informs the affected person what he/she is about to do and does the examination as gently as attainable. Note is made of any abnormalities of � the perianal skin � the presence or absence of o perianal skin tags o perianal warts o fistula in ano o pilonidial sinus o anal fissure o perianal hematoma o prolapsed strangulated piles o perianal abscesses Digital examination is then carried out after putting a beneficiant quantity of lubricant on the gloved index finger of the best hand. The pulp of the index finger is put flat on the anus 68 Physical Diagnosis and stress applied firmly and slowly in a slightly backwards direction. After preliminary resistance the anal sphincter relaxes and the finger could be handed into the anal canal. The finger is then handed into the rectum and the zero rectal wall assessed with sweeping movements of the finger via 360. In men, the rectovesical pouch, seminal vesicles and the prostate must be felt anteriorly. In women, the cervix is felt as a firm, rounded mass projecting again into the anterior wall of the rectum. On withdrawing the finger after rectal examination, look for proof of mucus, pus and blood on analyzing finger. This system is extra dependent than most on laboratory, histopathology and imaging strategies for completion of the diagnostic process. The basic ideas of clinical evaluation, nonetheless, nonetheless apply; acceptable and careful history taking and bodily examination are essential sixty nine Physical Diagnosis and can typically lead to a diagnosis. A related group of indicators and signs can arise in a affected person with alterations of the sex organs. There remains to be unwarranted stigma and disgrace connected to sexually transmitted diseases. The interview and examination should be carried out in privacy and with confidentiality. As with different clinical issues, diagnosis is achieved by history, examination and related investigation. It might radiate into the decrease quadrant of the abdomen and probably to the higher thigh and testicle or labium Hematuria: Is the presence of pink blood cells in the urine. Reddish discoloration of urine could also be as a result of the presence of pigments in the urine. Oliguria: Denotes the passage of lower than 400 ml of urine per day 70 Physical Diagnosis Anuria: Is the whole absence of urine output. Retention of urine must be excluded before a affected person is taken into account to have anuria. It is an arbitrary definition, on the idea of 24 hours urine output of greater than 3L per day. It could be grouped as: o Gonococcal urethritis o Non-gonococcal urethritis seventy one Physical Diagnosis Genital ulcer: this may be recurrent, single or a number of, painful or painless. Common causes include o chancre of primary syphilis o chancroid o genital herpes Other complaints � History of sores, growths on the penis � History of swelling or ache in the scrotum � Past history of sexually transmitted infections � History of sexual dysfunction the Female Genital Tract Vaginal discharge � could be related to itching � the colour, odor and quantity must be characterized Menstrual History: this part of history must be included. Various aspects must be thought-about including: � Regularity � Age at menarche (age on the onset of the first of the menstrual intervals) � Last menstrual interval � Length of time between intervals � How heavy is the flow o Estimate based mostly on the variety of pads or tampons used every day � Bleeding between intervals � History of discomfort of ache during times and severity, length of the ache when present seventy two Physical Diagnosis Sexual History: the sexual history could also be obtained after profitable the affected person�s confidence. The history should include: � Date of last sexual contact, particulars of contacts over latest months, risk of gay and bisexual contact and the kind of sexual practice are among the many things to be elicited upon history taking. Physical examination Urinary system Kidneys � Inspect the flanks for bruising or swelling � Assess each kidney for tenderness. List down the components that help in differentiating an enlarged left kidney from an enlarged spleen. Mention the components that help in differentiating ureteric ache from a pin arising from the kidneys. Barbara Bates, A Guide to Physical Examination and History Taking, Sixth Edition, 1995 7. And interpret the findings Introduction the lymph nodes are affected in some ways both immediately or not directly from diseases that originate in the lymphatic system itself or form another organ system. The lymphatic circulation is an alternative circulation system in which heavy molecular weight substances are carried again to the circulation from tissues, and obviously, it also serves as a filtration in phagocytosis and immunological activities. The lymphatic drainage in a given tissue or organ system is initially to certain group of lymph nodes. The accessible lymph node teams in our body for bodily examination are: Cervical lymph node teams Axillary lymph node teams Supraclavicular lymph node teams Inguinal lymph node teams Para aortic lymph node teams and others 78 Physical Diagnosis Cervical lymph node group: are affected normally by neck and face pathologies. They are also concerned in systemic sickness similar to lymphomas, tuberculosis, and pyogenic infections. Lymphomas Hard or soft in consistency depending up on the pathology Small or big dimension Associated with discharge and so forth Patients complain of swelling in the neck, over the angle of the jaw or any where in the neck. Cervical lymph group are also divided as: Anterior Posterior Deep or Superficial. Examination of the axillary lymph nodes: the Axillary lymph node teams are the commonly affected group by metastasis from breast carcinoma. Axillary lymph nodes are regularly concerned in pathologies, neoplastic or inflammatory origin. Examination of axillary lymph nodes is completed the affected person being finest in sitting position Pectoralis muscular tissues must be relaxed, Examiner sitting on the identical side of the axilla then Palpate systematically the five teams of lymph nodes. Examination of the inguinal lymph nodes: the inguinal lymph nodes are found along the inguinal canal. They typically are affected from infection around the decrease extremity and the exterior genitalia. Colorectal carcinoma metastasizes to these lymph nodes Pre trochlear nodes: Are located close to the elbow joint and affected by syphilis Examination of the Thyroid Gland Introduction the thyroid gland is located in the anterior neck connected to pretracheal fascia. It is composed of three lobes particularly left lobe, right lobe and connecting the 2 lobes is the isthmus lobe. The most typical pathology affecting the thyroid gland is iodine deficiency hyperplasia. However, different benign and malignant disorders might also produce enlargement of the thyroid gland. The following steps are followed as usual Inspection Size of the thyroid whether it is enlarged, (minimally, reasonably or severely) Movement with swallowing Any dominant or solitary nodule For scars, sinuses and change in color of the skin Palpation Palpation from in front (Fig 6. History: Common breast complaints are: o lump in the breast o breast ache o nipple discharge and o ulceration Age: Different breast pathologies are inclined to occur in several age teams. A breast lump in a young person is most likely to be a fibro adenoma, where as in elderly women it�s more likely to be cancer. Ask about: length any accompanying nipple discharged multiply the way it was first observed change in dimension elation to menses: clarification Breast ache: It is usually of functional and inflammatory origin. Ask about: o web site, which quadrant o severity o related swelling, lump, discharge o relation to menses (cyclic or non cyclic) o pregnancy, lactation 85 Physical Diagnosis Nipple discharge: Ask about: o color (bloody, serous, purulent, milky, and so forth) o spontaneous Vs non-Spontaneous o unilateral Vs bilateral o relation to menstrual cycle o related breast lump o drug intake E. Oral contraceptives Ask for any risk factor for cancer st o family history of breast cancer, 1 diploma relation o age at menarche (<12 years) o age at menopause (>fifty five years) o nulliparity o history of contra lateral breast cancer Ask for signs of metastatic disease (if cancer is suspected) o bone ache or swelling o cough, dyspnea, hemoptysis o jaundice o neurological abnormalities Physical Examination General ideas Should be accomplished in a personal place with good illumination Is extra informative if accomplished just after the top of menses affected person must be in a semi sitting position expose the whole of the higher half of the body at all times start from the conventional breast examine systematically, quadrant by quadrant Specific objectives of examination are to: detect and characterize breast mass or plenty 86 Physical Diagnosis elicit discharge from the nipple relate ache compliant to a specific breast discovering detect skin modifications detect enlarged axillary, supraclavicular or infraclavicular lymph nodes detect metastasis (If breast cancer suspected) Inspection: Stand in front of the affected person. Look on the: o dimension of breast o symmetry and contour of breast o nipple & areola for absence, symmetry, retraction, discharge o skin for retraction, discoloration, �peau d� orange� look nodules and ulceration � Repeat the inspection with the affected person raising her arms above the top. Palpation palpate with the palmar surface of your fingers roll the breast tissue between the chest wall and your hand palpate the whole breast quadrant by quadrant examine for o skin temperature o consistency of breast, nodularity o tenderness o nipple discharge (expression) o mass discrete or indiscrete Discuss the precise objectives of examination of the breast ninety Physical Diagnosis Reference: th 1. Barbara Bates, A Guide to bodily Examination and History Taking, Sixth version, 1995. Browse, An Introduction to the Symptoms and Signs of Surgical Disease, rd 3 version, 1997.
The affected person�s signs of pallor best allergy medicine 2012 cheap beconase aq amex, pale conjunctivae allergy guardian coupon order cheap beconase aq line, and systolic murmur are in keeping with anemia allergy to beer order genuine beconase aq line, which is confirmed by the laboratory findings allergy san antonio cheap 200MDI beconase aq amex. In a affected person with continual kidney disease, anemia is more than likely secondary to the disease course of. Option (A), 7-eight g/dL, and Option (B), 9-10 g/dL, are incorrect because hemoglobin ranges decrease than the target range are inadequate to alleviate signs of anemia. Option (D), 13-14 g/dL, and Option (E), 15-16 g/dL, are incorrect because hemoglobin ranges greater than the target range are related to elevated morbidity and mortality. Question 4 A 54-yr-outdated girl with diabetic nephropathy comes to the workplace because she has had vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, itching, and a metallic style in her mouth for the past two weeks. Additional studies in this affected person are more than likely to present presence of which of the next situations All rights reserved Sample Nephrology Questions & Critiques Critique this question exams the power of the examinee to associate acid-base abnormalities with particular medical situations. Chronic kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, and vomiting all lead to major metabolic acidosis. Option (A), hypokalemia, is wrong because as continual kidney disease progresses, the distal nephron loses the power to secrete potassium ions, most frequently resulting in hyperkalemia. Option (C), major metabolic alkalosis, is wrong because the development of continual kidney disease leads to distal renal tubular acidosis � marked by low blood pH, not elevated pH as seen in alkalosis. Question 5 A fifty six-yr-outdated man with a long historical past of alcohol use is admitted to the hospital after he had a seizure that was witnessed by his spouse. On physical examination, auscultation of the chest shows diminished breath sounds. Examination of the stomach shows firmness of the best upper quadrant, palpable hepatomegaly, and protuberance of the umbilicus. All rights reserved Sample Nephrology Questions & Critiques (B) Fluid restriction (C) Intravenous administration of 3% saline (D) Intravenous administration of 5% dextrose in water (E) Intravenous administration of diltiazem (Cardizem) Content Area: Renal Pathophysiology (15%) Critique this question exams the examinee�s ability to determine the most appropriate preliminary administration primarily based on signs, historical past, and laboratory findings. The presenting symptom of mental standing modifications along with the physical examination and laboratory findings point out that the seizure was more than likely secondary to hyponatremia. More fast increase in serum sodium degree is indicated in patients with hyponatremia when neurologic manifestations are current. Therefore, the most appropriate preliminary administration of the affected person�s situation is an intervention that may elevate sodium ranges � intravenous administration of 3% saline. Option (A), emergent hemodialysis, is wrong because no indicators for this therapy are current. Option (B), fluid restriction, is wrong because though this intervention will ultimately trigger a proportional increase within the serum sodium degree, the affected person�s mental standing modifications and seizure activity warrant more fast increase than fluid restriction alone could present. Option (D), intravenous administration of 5% dextrose in water, is wrong because this therapy will decrease the serum sodium degree. Question 6 A 67-yr-outdated man with stage 4 continual kidney disease, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and anemia of continual kidney disease comes to the workplace for routine observe-up. Measurement of which of the next additional laboratory values is most appropriate to screen for renal osteodystrophy in this affected person In the affected person with stage 4 continual kidney disease and corresponding abnormal laboratory values, the pathophysiologic response represents mineral bone disease and depletion of serum calcium. Option (D), serum thyroid-stimulating hormone degree, is wrong because this take a look at is used for diagnosing major and secondary hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, not mineral bone disease. Option (E), serum vitamin B12 degree, is wrong because this take a look at would be appropriate if anemia secondary to vitamin B12 deficiency were suspected. Question 7 A fifty six-yr-outdated girl comes to the emergency department because she has had growing swelling of the best ankle over the past two days, since she sustained an damage while enjoying outdoor together with her grandchildren. She says she has been taking over-the-counter ibuprofen 400 to 800 mg every 4 to six hours to relieve the pain. Medical historical past includes mild hypertension, which is at present controlled with lisinopril. Results of laboratory studies present elevated ranges of serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen. Acute renal failure induced by use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is suspected. If this suspected analysis is right, which of the next additional abnormal laboratory results is more than likely Question eight A 67-yr-outdated man with mild neurocognitive disorder (dementia), in whom peritoneal dialysis was just lately initiated because of end-stage renal disease, is dropped at the workplace by his spouse because he has had abdominal pain for the past 48 hours. On analysis, a pattern of fluid from the catheter is cloudy and grows gram-positive cocci. All rights reserved Sample Nephrology Questions & Critiques positive for gram-positive cocci. Therefore, the affected person�s symptom of abdominal pain is a sign of peritonitis and initiation of antibiotic therapy is the most appropriate next step. Option (B), intravenous administration of antibiotics, is believable however incorrect because the intraperitoneal route is most well-liked. Option (C), retraining of the affected person concerning catheter procedures, and Option (D), retraining of the affected person�s spouse concerning catheter procedures, are incorrect because though these are essential interventions, antibiotic therapy should be initiated first. Peritonitis should be managed before the affected person and/or his major caregiver can be educated concerning strategies of preventing recurrence of infection. The most appropriate next step is administration of peritonitis with intraperitoneal antibiotics, which are administered throughout peritoneal dialysis exchanges and never throughout hemodialysis. Question 9 A 60-yr-outdated girl with end-stage renal disease secondary to diabetic nephropathy comes to the clinic for routine hemodialysis. The affected person says she has cramping throughout hemodialysis in addition to weakness after each remedy. Development of cramps throughout hemodialysis and hypotension after hemodialysis are characteristic of extreme quantity elimination through the remedy. Increasing the dry weight will prevent extra quantity elimination and alleviate the related signs. Option (D), decrease the dialysis time, is wrong because even if the dialysis time is decreased, the same quantity of fluid will be eliminated and the affected person will continue to have cramping and hypotension. Question 10 A 38-yr-outdated girl with end-stage renal disease secondary to hypertension comes to the clinic for routine hemodialysis remedy. Blood stress previous to the remedy is 178/100 mmHg, and the affected person has a headache. Addition of ultrafiltration profiling is most appropriate for this affected person because it may enable for periods of equilibration of fluid within the vascular system and forestall cramping with out worsening hypertension. Option (A), continue lowering the target weight, is wrong because this intervention will trigger more quantity elimination and will likely worsen the cramping. Option (D), provoke sodium modeling, is wrong because this intervention is inappropriate in patients with hypertension. Sodium modeling helps decrease the incidence of postdialysis hypotension in addition to leg cramps and fatigue throughout and after the remedy. Medical historical past includes hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, stage three continual kidney disease, and kind 2 diabetes mellitus. Current medicines include carvedilol, amlodipine, furosemide, lisinopril, nitroglycerin transdermal patch, insulin, simvastatin, aspirin, and gabapentin. Which of the next findings in this affected person is the more than likely explanation for continued uncontrolled hypertension In a affected person with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, and kind 2 diabetes mellitus, for which appropriate drug therapies have been prescribed, the most appropriate preliminary suspected explanation for elevated blood stress (confirmed with bilateral measurements) is noncompliance with the drug routine. Question 12 A 32-yr-outdated man is referred to the workplace by his major care provider for preliminary consultation concerning stage three continual kidney disease. The affected person initially sought remedy on the major care workplace because he had pain in his decrease again. All rights reserved Sample Nephrology Questions & Critiques antihypertensive medicines. Before further evaluation concerning the reason for hypertension and decreased glomerular filtration rate, initiation of antihypertensive therapy is planned. Which of the next courses of medications is the most appropriate preliminary antihypertensive therapy for this affected person Option (A), alpha2-agonists, Option (C), beta-blockers, Option (D), calcium channel blockers, and Option (E), vasodilators, are all appropriate therapies for hypertension.
Raleigh Office:
5510 Six Forks Road
Suite 260
Raleigh, NC 27609
Phone
919.571.0883
Email
info@jrwassoc.com