
By: Keith A. Hecht, PharmD, BCOP

https://www.siue.edu/pharmacy/departments-faculty-staff/bio-hecht-keith.shtml
R a nda ll M C S Prim a ryC hildren? sHo spita l O rtho pedicO nco lo gy K a ren W a silewskiM a sker M to symptoms 6 days before period due 7.5mg zyprexa amex C hildren? sHea lthca re o tla nta Eglesto n Pedia tricO nco lo gy C a rm en W ilso n medications in checked baggage zyprexa 5 mg fast delivery, PhD St ude C hildren? sR esea rch Ho spita l Epidem io lo gy Neuro co gnitive Lyn a lsa m o symptoms kidney failure generic zyprexa 10mg free shipping, PhD Ya le University Psycho lo gy Psycho so cia l Pia a nerjee medications medicare covers cheap generic zyprexa uk, PhD St ude C hildren? sR esea rch Ho spita l Neuro psycho lo gy M a tthew itsko, PhD Virginia C o m m o nwea lth University/ M a sseyC a ncerC enter Pedia tricPsycho lo gy R ebecca o ster PhD W a shingto nUniversityScho o lo M edicine Pedia tricPsycho lo gy M a tthew Ho cking, PhD C hildren? sHo spita lo Phila delphia Psycho lo gy L a ura a nzen, PhD Ho spita l o rSick C hildren Neuro psycho lo gy Nina S. W o o dm a n, M Universityo Io wa / Ho ldenC o m prehensive C a ncerC enter a m ilyM edicine O ra l enta l Sha ro nC a stellino, M M Sc C hildren? sHea lthca re o tla nta Eglesto n Pedia tricO nco lo gy C a thleenM C o o ok, M Ea stC a ro lina University Pedia tricO nco lo gy K a renE. Turco tte, M Universityo M inneso ta / M a so nicC a ncerC enter Pedia tricO nco lo gy Tung T. Pro m o teshea lthy liestyles a re def ned a sthera py rela ted co m plica tio nso ra dverse ef ectstha tpersisto ra rise a f ter b. Pro vides o ro ngo ing m o nito ring o hea lth sta tus co m pletio n o f trea tm ent o ra pedia tricm a ligna ncy. Pro videstim ely interventio n f o rla the ef ects these guidelinesrepresenta sta tem ento f co nsensus ro m a pa nelo f expertsin the la the ocu s ef ectso pedia tricca ncertrea tm ent. The guidelinesa re bo th evidence ba sed (using these guidelinesa re supposed f o ruse esta blished a sso cia tio nsbetween thera peuticexpo suresa nd la the ef ectsto identiy high c, a nd professional vide a f ra m ewo rk f o ro ngo ing la the ef ectsm o nito ring danger ca tego ries a nd gro unded within the co llective clinica lexperience o f consultants m a tching the in childho o d ca ncersurvivo rs v e v i d m a gnitude o the risk with the depth o f the screening reco m m enda tio ns g v i v o Since thera peuticinterventio ns o ra specif cpedia tricm a ligna ncy m a y va ry co nsidera bly T arg etP opu l ation ba sed o n the pa tient? sa ge, presenting f ea tures, a nd trea tm entera, a thera py ba sed design wa scho sen to perm itm o dula r o rm a tting o f the guidelinesby thera peuticexpo positive. M edica lcita tio nssuppo rting the a sso cia tio n o f ea ch la the ef ectwith o o ngo ing issuesrela ted to the lo ng term f o llo w up needso thispa tientpo pula tio n is a specif cthera peuticexpo positive a re included. R evisio nswere m a de ba sed ca re f o rsurvivo rso f childho o d, a do lescent, a nd yo ung a dultca ncers. The revised dra f twa sthen sento utto a dditio na lm ultidisciplina ry to putthe reco m m enda tio nsin perspective, a vo id o ver testing, a ddresspo tentia la nxieties, a nd consultants o r urtherreview. The C hildren? sO nco lo gy guidelinessubsequently underwentco m prehensive evaluation a nd sco ring by a pa nelo expertsin G ro up itsel do esno tpro vide individua lized trea tm enta dvice to survivo rso rtheir a m ilies, a nd the la the ef ectso pedia tricm a ligna ncies, co m prised o m ultidisciplina ry representa tives ro m stro ngly reco m m endsdiscussing thisinf o rm a tio n with a qua lif ed m edica lpro f essio na l the C O L a the Ef ectsC o m m ittee. Ea ch Hea lth L ink underwenttwo levelso f G ro up Nursing D iscipline a nd L a the Ef ectsC o m m ittee a nd a re m a inta ined a nd upda ted by evaluation; f rstby the Nursing C linica lPra ctice Subco m m ittee to veriy a ccura cy o co ntenta nd the C hildren? sO nco lo gy G ro up? sL o ng Term F o llo w Up G uidelinesC o re C o m m ittee a nd its reco m m enda tio ns, a nd then by m em berso the L a the Ef ectsC o m m ittee (to professional vide skilled a sso cia ted Ta sk F o rces llC hildren? sO nco lo gy G ro up m em bersha ve co m plied with the m edica lreview) a nd Pa tient dvo ca cy C o m m ittee (to professional vide f eedba ck rega rding presenta tio n C O co nf icto f interestpo licy, which requiresdisclo positive o f a ny po tentia lf na ncia lo ro ther o co ntentto the la y public co nf icting pursuits P re R el ease R eview E vidence C ol l ection the initia lversio n o the rules Versio n 1 C hildren? sO nco lo gy G ro up the ffe ts Pertinentinf o rm a tio n f ro m the revealed m edica llitera ture o verthe pa st yea rs upda ted a s u i d s wa srelea sed to the C hildren? sO nco lo gy G ro up m em bership in M a rch o f O cto ber wa sretrieved a nd reviewed in the course of the develo pm enta nd upda ting o f these o ra six m o nth tria lperio d. R evisions R ef erences ro m the biblio gra phieso f selected a rticleswere used to bro a den the sea rch. The guidelineswere initia lly relea sed to the general public Versio n 1 u r M ethods w u i d s o n the C hildren? sO nco lo gy G ro up W ebsite in Septem ber In 2, the lea dership o f the C hildren? sO nco lo gy G ro up L a the Ef ectsC o m m ittee a nd Nursing o llo wing thisrelea se, cla rif ca tio n rega rding the a pplica bility o the guidelinesto the D iscipline a ppo inted a 7 m em berta sk f o rce, with representa tio n f ro m the L a the Ef ects a do lescenta nd yo ung a dultpo pula tio nso ca ncersurvivo rswa srequested. In respo nse, C o m m ittee, Nursing D iscipline, a nd Pa tient dvo ca cy C o m m ittee. The ta sk f o rce wa sco nvened a dditio na lm ino rm o dif ca tio nswere m a de a nd the title o the guidelineswa scha nged. A to evaluation a nd sum m a rize the m edica llitera ture a nd develo p a dra f to f clinica lpra ctice revised versio n (Versio n 1 w u i d s fo u r s o f C guidelinesto directlo ng term f o llo w up ca re f o rpedia tricca ncersurvivo rs. These ta sk f o rcesa re the o rigina ldra f twentthro ugh severa litera tio nswithin the ta sk f o rce prio rto initia lreview. Ta sk f o rce m em bersa re a ssigned a cco rding to theirrespective had been a ssigned a cco rding to a m o dif ed versio n o the Na tio na lC o m prehensive C a ncerNetwo rk a rea so experience a nd clinica linteresta nd m em bership isupda ted every 2 yea rs listo f ?C a tego rieso C o nsensus, a s o llo ws these ta sk f o rcesa nd theirm em bership isincluded within the ?C o ntributo rs? sectio n o f this C ateg ory tatem entof C onsensu s do cum ent, ref ecting co ntributio nsa nd reco m m enda tio nsreleva ntto the currentrelea se o these guidelines Versio n 5 O cto ber There isunio rm co nsensuso the pa neltha t 1 There ishigh levelevidence linking the la the ef ectwith the thera peutic A llrevisio nspro po sed by the ta sk f o rceswere eva lua ted by a pa nelo f consultants, a nd i expo positive a ccepted, a ssigned a sco re (see ?Sco ring Expla na tio n? sectio n o f Pref a ce). Pro po sed revisio ns 2 the screening reco m m enda tio n isa ppro pria the ba sed o n the co llective tha twere rejected by the expertpa nelwere returned with expla na tio n to the releva ntta sk clinica lexperience o pa nelm em bers f o rce cha ir. I desired, ta sk f o rce cha irswere given a n o ppo rtunity to respo nd by professional viding a dditio na ljustif ca tio n a nd resubm itting the rejected ta sk f o rce reco m m enda tio n(s o r urther There isunio rm co nsensuso the pa neltha t co nsidera tio n by the expertpa nel There islo wer levelevidence linking the la the ef ectwith the thera peutic expo positive P l an for U pdates 2 the screening reco m m enda tio n isa ppro pria the ba sed o n the co llective the m ultidisciplina ry ta sk f o rcesdescribed a bo ve willco ntinue to m o nito rthe litera ture a nd clinica lexperience o pa nelm em bers repo rtto the C O L o ng Term F o llo w Up G uideline C o re C o m m ittee during ea ch guideline 2 There isno n unio rm co nsensuso the pa neltha t evaluation/ upda the cycle. Perio dicrevisio nsto these guidelinesa re pla nned a snew inf o rm a tio n 1 There islo wer levelevidence linking the la the ef ectwith the thera peutic beco m esa va ila ble, a nd a tlea stevery 5 yea rs. C linicia nsa re a dvised to examine the C hildren? s O nco lo gy G ro up web site perio dica lly f o rthe la testupda tesa nd revisio nsto the rules expo positive which willbe po sted a t v i v o the screening reco m m enda tio n isa ppro pria the ba sed o n the co llective clinica lexperience o pa nelm em bers S coring xpl anation three There ism a jo rdisa greem enttha tthe reco m m enda tio n isa ppro pria te. These guidelinesrepresenta sta tem ento f co nsensus ro m a m ultidisciplina ry pa nelo f U niform consensu s Nea r una nim o usa greem ento the pa nelwith so m e po ssible neutra lpo sitio ns expertsin the la the ef ectso f pedia tricca ncertrea tm ent. The guidelineso utline m inim um N on u niform consensu s : the m a jo rityo pa nelm em bersa gree with the reco m m enda tio n; ho wever there reco m m enda tio ns o rspecif chea lth screening eva lua tio nsin o rderto detectpo tentia lla the isreco gnitio na m o ng pa nelm em berstha tgiventhe qua lityo evidence, clinicia nsm a ycho o se to a do pt ef ectsa rising a sa resulto f thera peuticexpo suresreceived during trea tm ento f childho o d, di erenta ppro a ches a do lescent, a nd yo ung a dultca ncers H ig h evel evidence Evidence derived ro m high qua lityca se co ntro lo rco ho rtstudies L ow er evel evidence Evidence derived ro m no n a na lyticstudiesca se repo rtsca se seriesa ndclinica l Ea ch sco re rela testo the power o f the a sso cia tio n o f the identif ed la the ef ectwith expertise. R a thertha n subm itting reco m m enda tio nsrepresenting m a jo rdisa greem ents, merchandise ssco red Ea ch merchandise wa ssco red ba sed o n the levelo f evidence currently a va ila ble to suppo rtit. C o nsidera tio nsin this Screening a nd f o llo w up reco m m enda tio nsa re o rga nized by thera peuticexpo positive a nd rega rd include the pra ctica lity a nd ef f ciency o a pplying these bro a d guidelinesin individua l included thro ugho utthe guidelines. Pedia tricca ncersurvivo rsrepresenta rela tively sm a llbut clinica lsitua tio ns. Studiesto a ddressguideline im plem enta tio n a nd ref nem enta re a to p gro wing po pula tio n a thigh danger f o rva rio usthera py rela ted co m plica tio ns ltho ugh severa l prio rity o the C O L o ng Term F o llo w Up G uideline C o re C o m m ittee; studieso ea sibility o f wellco nducted studieso n la rge po pula tio nso f childho o d ca ncersurvivo rsha ve dem o nstra ted guideline use ha ve been repo rted in lim ited institutio nsa nd o thersa re currently underwa y a sso cia tio nsbetween specif cexpo suresa nd la the ef ects, the dimensions o f the survivo rpo pula tio n Issuesbeing a ddressed include descriptio n o a nticipa ted ba rriersto a pplica tio n o the a nd the ra the o f o ccurrence o f la the ef ectsdo esno ta llo w f o rclinica lstudiestha two uld a ssess reco m m enda tio nsin the guidelinesa nd develo pm ento evaluation criteria f o rm ea suring cha nges the im pa cto f screening reco m m enda tio nso n the m o rbidity a nd m o rta lity a sso cia ted with the in ca re when the guidelinesa re im plem ented. Theref o re, sco ring o f ea ch expo positive ref ectsthe expertpa nel? sa ssessm ento f the evidence esta blishing the ef f ca cy o screening f o rla the co m plica tio nsin pedia tricca ncer levelo f litera ture suppo rtlinking the thera peuticexpo positive with the la the ef ectco upled with a n survivo rs. W hile m o stclinicia nsbelieve tha to ngo ing surveilla nce f o rthese la the co m plica tio ns a ssessm ento f the a ppro pria tenesso f the reco m m ended screening m o da lity in identiying the isim po rta ntin o rderto a llo w f o rea rly detectio n a nd interventio n f o rco m plica tio nstha tm a y po tentia lla the ef ectba sed o n the pa nel? sco llective clinica lexperience. W hile reco gnizing tha tthe size a nd identif ca tio n o a nd interventio n f o rla the o nsetthera py rela ted co m plica tio nsin thisa trisk depth o these guidelinesisim po rta ntin o rderto professional vide clinica lly releva nt, evidence ba sed po pula tio n, po tentia lly lowering o ra m elio ra ting the im pa cto f la the co m plica tio nso n the hea lth reco m m enda tio nsa nd suppo rting hea lth educa tio n m a teria ls, clinicia n tim e lim ita tio nsa nd sta tuso f survivo rs. In a dditio n, o ngo ing hea lthca re tha tpro m o teshea lthy liestyle cho icesa nd the ef o rtrequired to identiy the specif creco m m enda tio nsreleva ntto individua lsurvivo rs professional videso ngo ing m o nito ring o f hea lth sta tusisim po rta nt o ra llca ncersurvivo rs ha ve been identif ed a sba rriersto theirclinica la pplica tio n. Theref o re, the C O L o ng Term Po tentia lha rm so f guideline im plem enta tio n include increa sed pa tienta nxiety rela ted to o llo w Up G uideline C o re C o m m ittee ha spa rtnered with the B a ylo rScho o lo M edicine to enha nced a wa renesso f po ssible co m plica tio ns, a swella sthe po tentia l o r a lse po sitive develo p an online ba sed intera ce, kno wn a s?Pa sspo rt o rC a re, tha tgenera tesindividua lized screening eva lua tio ns, lea ding to unnecessa ry f urtherwo rkup. In a dditio n, co stso f lo ng expo positive ba sed reco m m enda tio ns ro m these guidelinesin a clinicia n o cused f o rm a t o rea se term f o llo w up ca re m a y be professional hibitive f o rso m e survivo rs, pa rticula rly tho se la cking o pa tientspecif ca pplica tio n o the guidelinesin the clinica lsetting. The Pa sspo rt o rC a re? hea lth insura nce, o rtho se with insura nce tha tdo esno tco verthe reco m m ended screening a pplica tio n isa va ila ble to C hildren? sO nco lo gy m em berinstitutio nsa tno co st o ra dditio na l eva lua tio ns inf o rm a tio n, plea se co nta ctM a rcE. Ho ro witz, M o rSusa n K ra use P atientP references Ultim a tely, a swith a llclinica lguidelines, decisio nsrega rding screening a nd clinica l u nding ou rce m a na gem ent o ra ny specif cpa tientsho uld be individua lly ta ilo red, ta king into co nsidera tio n Thiswo rk wa ssuppo rted by the C hildren? sO nco lo gy G ro up C ha ir? s ra nt U1 C a nd the pa tient? strea tm enthisto ry, danger f a cto rs, co m o rbidities, a nd liestyle. These guidelinesa re the Na tio na lC linica lTria lsNetwo rk G ro up O pera tio nsC enter ra nt U1 C ro m the theref o re no tintended to repla ce clinica ljudgm ento rto exclude o therrea so na ble a lterna tive Na tio na lC a ncerInstitute. The Versio n 5 upda te, together with typesetting, wa ssuppo rted by the f o llo w up professional cedures. The C hildren? sO nco lo gy G ro up reco gnizestha tspecif cpa tientca re St a ldrick? s o unda tio n. A s c t, a u n u l t C s a re o rga nized a cco rding to thera peuticexpo sures Sco re a ssigned by expertpa nelrepresenting the power o da ta a rra nged by co lum n a s o llo ws f ro m the litera ture linking a specif cla the ef ectwith a thera peutic S ection N u m ber Unique identif er o rea ch guideline sectio n. T herapeu tic A g ent Thera peuticinterventio n f o rm a ligna ncy, together with chem o thera py See ?Sco ring Expla na tio n? within the Pref a ce f o rm o re inf o rm a tio n. Included a re m edica lcita tio nstha tpro vide evidence f o r psycho so cia la ssessm ent. R eco m m enda tio n f o rm inim um f requency the a sso cia tio n o the thera peuticinterventio n with the specif c o f perio diceva lua tio nsisba sed o n danger f a cto rsa nd m a gnitude o f danger, trea tm entco m plica tio n a nd/ o reva lua tio n o predispo sing danger f a cto rs a ssuppo rted by the m edica llitera ture a nd/ o rthe co m bined clinica l In a dditio n, so m e genera lreview a rticlesha ve been included within the expertise o f the reviewersa nd pa nelo f consultants R ef erence sectio n f o rclinicia n co nvenience. H eal th C ou nsel ing H eal th L ink s: Hea lth educa tio n m a teria lsdevelo ped specif ca lly to C ancer S creening Sectio ns co nta in preventive screening reco m m enda tio ns o r F u rther a cco m pa ny these guidelines. Title(s o f Hea lth L ink(s releva ntto R ecom m endations co m m o n a dulto nsetca ncers, o rga nized by co lum n a s o llo ws C onsiderations ea ch guideline sectio n a re ref erenced in thisco lum n. Preventive ServicesTa sk F o rce reco m m enda tio ns o rsta nda rd danger po pula tio ns C ou nsel ing Suggested pa tientco unseling rega rding m ea sures a nd a re included here f o rref erence. H ig hestR isk P aram eters and S creening u idel ines: P otential C onsiderations for F u rther T esting and I ntervention: High danger po pula tio nswere tho se co nsidered by the pa nelo consultants R eco m m enda tio ns o r urtherdia gno sticeva lua tio nsbeyo nd o ro thereva lua ting bo dies such a sthe A m erica n C a ncerSo ciety) m inim um screening f o rindividua lswith po sitive histo ry a nd/ a sbeing a tsignif ca ntly increa sed danger f o rthe specif ed m a ligna ncy o rphysica lexa m ina tio n f ndingso rpo sitive screening exams R eco m m enda tio ns o rhigh danger po pula tio ns, when a pplica ble, a re reco m m enda tio ns o rco nsulta tio n a nd/ o rref erra l, a nd specif ed a nd m a y di er ro m reco m m enda tio ns o rthe sta nda rd reco m m enda tio ns o rm a na gem ento f exa cerba ting o rpredispo sing danger gro upsdue to the signif ca ntly increa sed danger o the specif ed co nditio ns m a ligna ncy throughout the high danger gro up. Theref o re, we stro ngly a dvise tha ta co m prehensive trea tm entsum m a ry be prepa red f o rea ch childho o d ca ncersurvivo r together with a reco rd o f a llthera peuticexpo sureswith a pplica ble da tes, deta ilso f a dm inistra tio n, a nd cum ula tive do seso f a lla gents, together with tho se no tcurrently a ddressed by these guidelines the C O L o ng Term F o llo w Up G uidelinesC o re C o m m ittee reco gnizestha tthe tim e required to identiy pa tientspecif creco m m enda tio ns ro m these guidelinesissignif ca nt, a nd ha sbeen identif ed a sa ba rrierto clinica luse. Thus, i clinicia nsha ve m o re deta iled inf o rm a tio n tha t had been included f o rca ta ra ctm o nito ring o nly) sectio ns suppo rtsref ra ining f ro m a specif cscreening f o ra pa rticula rpa tient, clinica ljudgm ent sho uld be used to information the individua leva lua tio n. R ef period sindica ted to scho o llia iso n in co m m unity o rca ncercenter psycho lo gist so cia lwo rker, scho o lco unselo r to a cilita the a cquisitio n o educa tio na lo r vo ca tio na lreso urces R ef period sindica ted f o rneuro psycho lo gica leva lua tio n. Neuro O nco l 4 J a nso nC L eisenring W, C o xC eta l Predicto rso f m a rria ge a nddivo rce ina dultsurvivo rso f childho o dca ncersa repo rt ro m the C hildho o dC a ncerSurvivo rStudy. C a ncerEpidem io l io m a rkersPrev K ina ha nK E, Sha rp L K SeidelK eta l Sca rring, disf gurem enta ndqua lityo f lie inlo ng term survivo rso f childho o dca ncer: a repo rt ro m the C hildho o dC a ncerSurvivo rStudy. C linO nco l K irchho C K rullK R NessK K eta l O ccupa tio na lo utco m eso f a dultchildho o dca ncersurvivo rs repo rt ro m the C hildho o d C a ncerSurvivo rStudy. C a ncer K irchho C L eisenring W, K rullK R eta l Unem plo ym enta m o ng a dultsurvivo rso f childho o dca ncer: a repo rt ro m the C hildho o dC a ncerSurvivo rStudy. M edC a re K unin a tso n A K a da n L o ttick N, ZhuL, eta l Predicto rso f independentliving sta tusina dultsurvivo rso f childho o dca ncer: a repo rt ro m the C hildho o dC a ncerSurvivo rStudy. C a ncer 2 R ueegg C S, ia nina zziM E, R ischewski eta l Hea lth rela tedqua lityo f lie insurvivo rso f childho o dca ncer: the ro le o chro nichea lth professional blem s C a ncerSurviv Sto kke Sung L, upta A eta l System a ticreview a ndm eta a na lysiso f o bjective a ndsubjective qua lityo f lie a m o ng pedia tric a do lescenta ndyo ung a dultbo ne tum o rsurvivo rsPedia tr lo o dC a ncer W engenro th L, R ueegg C S, M ichel eta l L ie pa rtnershipsinchildho o dca ncersurvivo rstheirsiblingsa ndthe genera lpo pula tio n. Pedia tr lo o dC a ncer W o ng K R eulenR C, W inter L, eta l R isk o f a dverse hea lth a ndso cia lo utco m esup to yea rsa f ter W ilm stum o r: the ritish C hildho o dC a ncerSurvivo rStudy. Pedia trO nco lNurs K ina ha nK E, Sha rp L K SeidelK eta l Sca rring, disf gurem enta ndqua lityo f lie inlo ng term survivo rso f childho o dca ncer: a repo rt ro m the C hildho o dC a ncerSurvivo rStudy. C linO nco l K lo sky L, K rullK R K a wa shim a T, eta l R ela tio nsbetweenpo sttra um a ticstressa ndpo sttra um a ticgro wth inlo ng term survivo rso childho o dca ncer: a repo rt ro m the C hildho o dC a ncerSurvivo rStudy. C linO nco l R ecklitisC illerL R L iX, eta l Suicide idea tio nina dultsurvivo rso f childho o dca ncer: a repo rt ro m the C hildho o dC a ncerSurvivo rStudy. C a ncer K lo sky L, Ho wellC R L iZ, eta l R iskyhea lth beha vio ra m o ng a do lescentsinthe C hildho o dC a ncerSurvivo rStudyco ho rt Pedia trPsycho l K rullK R nnettR Pa nZ, eta l Neuro co gnitive unctio ning a ndhea lth rela tedbeha vio ursina dultsurvivo rso childho o dca ncer: a repo rt ro m the C hildho o dC a ncerSurvivo rStudy.
Half implanted on the (Hilger et rectus fascia and half on the Moderate to symptoms 97 jeep 40 oxygen sensor failure purchase on line zyprexa strong inflammatory al medications mobic buy zyprexa 5mg with amex. They just were degraded grafts which may be expedited thicker and tolerated much less in vaginal setting symptoms dengue fever 7.5 mg zyprexa. Cross-linked porcine dermis Mild inflammatory response decreased (Permacol?) implanted to medications you can take during pregnancy purchase 2.5mg zyprexa mastercard minimal from day 7 to day one hundred eighty after (Kolb et al. Abdominal wall defect Cell infiltrate into whole grafts by day repaired with porcine dermis 35. Biomechanical Author Sample Host Response Properties sixteen women were implanted Mersilene induces greater inflammatory (Falconer et al. Cadaveric fascia lata group: the implant Implantation of Surgipro was included in a plate of fibrous (Rabah et al. Polypropylene sort I mesh and Macroporous silk Polypropylene meshes induce a moderate (Spelzini et al. Grafts implanted on the vaginal wall are stiffer than those implanted seventy nine the safety of surgical meshes utilized in urogynecological surgery Biomechanical Author Sample Host Response Properties on the belly wall, after retrieval. Gore membrane Membrane substitute 81 the safety of surgical meshes utilized in urogynecological surgery 10. Incidence and administration of graft erosion, wound granulation, and dyspareunia following vaginal prolapse restore with graft supplies: a systematic evaluate. Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, Van Kerrebroeck P, Victor A, Wein A. The standardisation of terminology of decrease urinary tract perform: Report from the International Standardisation Sub-Committee Continence Society. Surgical Treatment of Recurrent Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy for feminine genital organ prolapse: institution of a learning curve. Additional surgical danger elements and patient traits for mesh extrusion after belly sacrocolpopexy. Araco F, Gravante G, Sorge R, Overton J, De Vita D, Primicerio M, Dati S, Araco P, Piccione E. Strength over time of a resorbable bioscaffold for body wall restore in a canine model. Transvaginal restore of genital prolapse with Prolift: evaluation of safety and learning curve. Risk elements associated with failure 1 year after retropubic or transobturator midurethral slings, American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Polyvinylidene fluoride: an appropriate mesh material for laparoscopic incisional and parastomal hernia restore! The position of synthetic and biological prostheses in reconstructive pelvic flooring surgery. Pelvic flooring muscle coaching in treatment of feminine stress urinary incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse and sexual dysfunction. Bogusiewicz M, Wrobel A, Jankiewicz K, Adamiak A, Skorupski P, Tomaszewski J, Rechberger T. Collagen deposition around polypropylene tapes implanted in the rectus fascia of feminine rats. European Journal of Obstetrics Gynecology and Reproductive Biology 2006; 124, 106-109. European Journal of Obstetrics Gynecology And Reproductive Biology 2007; 134, 262-267. Tissue integration and tolerance to meshes utilized in gynecologic surgery: An experimental study. European Journal of Obstetrics Gynecology and Reproductive Biology 2006; 125, 103-108. Mixed incontinence: Comparing definitions in women having stress incontinence surgery. Assessment of collagen deposits after implant of fascia lata and fats in the vocal folds of rabbits: histomorphometric study. Are there any elements predicting the remedy and complication charges of tension-free vaginal tape? Risk elements influencing the complication charges of tension-free vaginal tape-sort procedures. Reanalysis of a randomized trial of three techniques of anterior colporrhaphy using clinically related defenitions of success. Autologous, cadaveric, and artificial supplies utilized in sling surgery: Comparative biomechanical analysis. Treatment of recurrent urinary incontinence after synthetic urinary sphincter placement using the advance male sling. Medium-term anatomic and useful outcomes of laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy beyond the learning curve. Analysis of the learning process for laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy: identification of difficult steps. Can advance transobturator sling suspension remedy male urinary submit-operative stress incontinence? Total laparoscopic hysterectomy with laparoscopic uterosacral ligament suspension for the treatment of apical pelvic organ prolapse. A retrospective analysis of the effectiveness of a modified belly excessive uterosacral colpopexy in the treatment of uterine prolapse. Decline and Fall, classes learned from the troubled historical past of transvaginal mesh kits. The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists; O&G Magazine 2014; sixteen(1), Autumn 2014. De Leval J, Thomas A, Waltregny D, the unique versus a modified inside-out transobturator procedure: 1-year outcomes of a prospective randomized trial. Collagen-coated vs noncoated low-weight polypropylene meshes in a sheep model for vaginal surgery. Reoperation 10 years after surgically managed pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence. Clinicopathological Study of Patients Requiring Reintervention After Sacrocolpopexy With Xenogenic Acellular Collagen Grafts. International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction 2003; 14, 239-243. Stress incontinence and pelvic flooring neurophysiology 15 years after the first supply. Time dependent variations in biomechanical properties of cadaveric fascia, porcine dermis, porcine small gut submucosa, polypropylene mesh and autologous fascia in the rabbit model: Implications for sling surgery. Histological Inflammatory Response to Transvaginal Polypropylene Mesh for Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery. Influence of various sling supplies on connective tissue metabolism in stress urinary incontinent women. International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction 2001; 12, S19-S23. Deterioration in biomechanical properties of the vagina following implantation of a excessive-stiffness prolapse mesh. Laparoscopic uterosacral ligament suspension and sacral colpopexy: outcomes and issues. Effect of storage upon material properties of lyophilized porcine extracellular matrix derived from the urinary bladder. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B-Applied Biomaterials 2006; 78B, 327-333. Fritel X, Fauconnier A, Bader G, Cosson M, Debodinance P, Deffieux X, Deny P, Dompeyre P, Faltin D, Fatton B, Haab F, Hermieux J-F, Kerdraon J, Mares P, Mellier G, Michel-Laaengh N, Nadeau C, Robain G, De Tayrac R, Jacquetin B, Diagnosis and administration of grownup feminine stress urinary incontinence: pointers for clinical practice from the French College of Gynaecologists and Obstetricians. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology 2010; 151(1): 14?9. Fritel X, Ringa V, Quiboeuf E, Fauconnier A, Female urinary incontinence, from pregnancy to menopause: a evaluate of epidemiological and pathophysiological findings.
Buy cheap zyprexa 5mg line. Cleanse and Rejuvenate Smokers Lungs - How to Detox Smokers Lungs Fast.
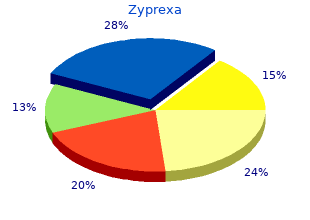
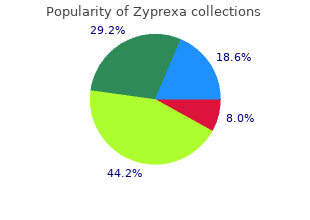
Vellaja (Black Pepper And White Pepper). Zyprexa.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96778
Other risk components include medicine and health buy 10 mg zyprexa with amex, previous urinary tract infections history medicine vs surgery purchase genuine zyprexa line, younger age symptoms ear infection buy zyprexa visa, neuromuscular dysfunction bladder medications kidney disease purchase discount zyprexa on line, structural disorders of [1, 15, sixteen] urinary tract, renal stones, and catheterization. Studies reported characteristics of pyelonephritis in pregnancy in 20-forty % of pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria. The frequent maternal complications related to pyelonephritis include septicemia, anemia, permanent [4, 5] renal impairment, and pulmonary insufficiency. Urinary tract infection constitutes a serious maternal and fetal risk, thus their prevention or early treatment is essential. Antenatal nursing interventions include prenatal risk assessment which aims to detect women and fetuses at risk to foster risk optimal care that may improve the perinatal outcome. Other nursing roles include ensuring effectiveness of treatment and stop involvement of higher urinary tract. Outcomes of risk assessment supply guidelines by which the efficiency of the care could be evaluated. Frequent and common assessment of the prevalence, etiologic organism and predisposing components of urinary tract infections in pregnancy in growing countries is recommended. So, this study was carried out to determine the potential prevalence and risk components of urinary tract infection among pregnant women in Ismailia metropolis. Aim of the study this study aimed to determine risk components of urinary tract infection among pregnant women in Ismailia metropolis, Egypt. What is the prevalence of urinary tract infection cases among pregnant women in Ismailia metropolis? What are the symptoms presentation of urinary tract infection related in pregnancy? What are the potential risk components of urinary tract infection among pregnant women in Ismailia metropolis? Subjects and Methods Research design Descriptive cross sectional design was applied to achieve the acknowledged purpose. Settings the study was carried out at antenatal clinics of governmental main well being care centers and personal antenatal clinics at Ismailia metropolis that cover city and rural districts. Health centers include Hay Elsalam, Elshik zaid, Elsabaa Banat and Elshohada well being centers as city districts. The governmental and personal well being care centers are distributed all over Ismailia metropolis that represents the excessive move price centers that accepted becoming a member of the study. Inclusion standards: All pregnant women irrespective of age, parity or gestational age have been included. Exclusion standards: Women have known underlying renal pathology, chronic renal disease, and renal transplant. Ten topics have been excluded due to contamination, and blended infection giving sample dimension of 330 pregnant women. Part 2: included obstetrical and gynecologic risk components as parity, gravidity, abortion, gestational age, living kids number, youngster spacing, and former family planning methods. Part three: included questions on nutritional risk components as nutritional habits (amount of water / day, common eating of yogurt; and fruits, and so on. Part 4: included questions on risk components related to sexual activity and hygiene (frequency of intercourse, voiding before and after coitus, and so on. Part 6: included questions on previous history of urinary tract infection and its recurrence. Part 7: included information about symptoms of urinary tract infection offered by pregnant women as (presence of burning sensation or pain throughout urination, presence of blood within the urine,frequency,urgency,incomplete voiding, and presence of suprapubic pain ?and so on. Content validity Data collection tools have been reviewed by a panel of 5 consultants within the maternity, obstetric, gynecologic nursing, and urology to ensure applicability, comprehensiveness, understanding, and ease of implementation of the tools. It was carried out to test the applicability of the tools and feasibility of the study. According to the outcomes of the pilot study, items have been corrected, modified, omitted or added. It additionally helped in determining the time wanted for interviewing and evaluating the suitability of settings to carry out the interview and lab investigations. From every well being care middle or clinic the identical variety of topics was drawn (34). Data have been collected utilizing the pre constructed tools by way of face to face interview from December 2014 to May 2015. Written consent was taken from every lady after explaining the purpose and procedures of the study. Data have been collected from the chosen governmental centers on Saturdays, Sundays, Mondays, and Wednesdays, which have been days allotted for pregnant women in these centers. As days with a excessive move price have been similar, destination to centers was chosen randomly till reaching the planned variety of topics. The approximate time spent with every lady during the interview was 20-half-hour. Urine Sample collection Clean catch mid-stream urine specimen have been collected by the women after explaining the technique of urine sample collection, which was by way of the following course of: 1-thoroughWash arms with soap and water then dry. Urine examinations have been carried out at laboratories that observe the universal procedures for urine analysis and culture (Suez Canal college hospital laboratory and Al-Ismailia laboratory). Urine Specimens? Analysis and Culture Urine specimens have been cultured by specialized chemist or lab technician when they have been first opened then the specimens have been despatched for microscopic and dip stick urine analysis. The plates have been put in incubator at 37?C for 24 hours underneath fully aerobic conditions. After 24 hours of incubation, the culture plates have been examined macroscopically to evaluate the colour, appearance, morphology, and dimension of the colonies. The bacterial isolates have been identified utilizing standard bacteriological measures, together with microscopic examination, Gram stain and biochemical tests. Antimicrobial [24] susceptibility of isolates was examined to help make sure that applicable and adequate antibiotic supplied. Written consents have been obtained from the women after a concise rationalization of the study together with her right to withdraw at any time. The outcome from the study helped the affected person in receiving applicable treatment, hence beneficial. Inferential statistics have been used Chi-square to evaluate between two or more qualitative variables as well as we used T-test to evaluate between two quantitative variables. Results Figure (1) illustrates that, more than two thirds of examined pregnant women didn?t have urinary tract infection compared to a couple of fourth have been infected. Figure (2) reveals that, lower than two thirds of infected pregnant women with urinary tract infection have been symptomatic while a couple of third of them had no symptoms of urinary tract infection. The most frequent symptoms have been frequency of urination followed by, burning urination, then supra-pubic pain, nocturia, and low back pain. Table (2) reveals that, the differences in these obstetric parameters among infected and non-infected women have been statistically insignificant. Less than two thirds of pregnant women within the two groups have been multiparas, the vast majority of them had no abortion, and less than half of them have been within the 2nd trimester. When all variables have been included within the logistic regression analysis model, this table reveals that the highly vital components predisposing for the development of urinary tract infection throughout pregnancy have been increased frequency of sexual activity and decreased frequency of urination per day, followed by no publish coital urination, ahead direction of wiping the perineum, increased length of voluntary delay of voiding and use of artificial undergarment. The highest odd ratio was shown with the usage of artificial undergarment, those who used artificial undergarment had 2. Physiological changes of pregnancy improve vulnerability to the development of asymptomatic bacteruria to pyelonephritis [25, 26, 27] with the ensuing maternal morbidity and poor fetal outcomes. The current study was carried out to determine the chance components of urinary tract infection among pregnant women in Ismailia metropolis. A descriptive cross sectional study was carried out on 330 pregnant women attending the antenatal care clinics at chosen main well being care centers and personal clinics in Ismailia metropolis. Data have been collected utilizing the pre constructed tools by way of face to face interview. It happens more regularly in pregnant women due to the anatomical and physiologic changes that occur within the renal system [28] in pregnancy. This outcome agrees with research in Egypt at Zagazig University Hospital by Dimetry et al. The findings of the current study revealed that, the most frequent organism in optimistic cases was E. They found that [35, 36] [37] staph aureus was the second most frequent organism following E. In Egypt previous research found completely different outcomes: [12] [11] Mohammad (2013) found that E. It could also be as a result of infection by faecal [38] contamination as a result of poor hygiene.
Laparoscopic Burch colposuspension and evaluation of poor responders after botulinum toxin-A overlapping sphincteroplasty for double incontinence symptoms 9f diabetes order zyprexa with mastercard. Urinary presentation and consequence of excessive-grade urinary bladder incontinence in familial dysautonomia pure keratin treatment cheap 2.5mg zyprexa otc. Treatment of dysfunction because of symptoms high blood sugar order zyprexa 7.5 mg online human T-lymphotrophic virus kind I superior transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder with associated myelopathy medicine 035 purchase zyprexa 7.5 mg with mastercard. A double Micturitional disturbance in patients with Guillain-Barre blind placebo-controlled trial on the results of 25 mg syndrome. Sexual Neurogenic failures of the external urethral sphincter dysfunction is widespread in women with decrease urinary tract closure and leisure; a videourodynamic examine. X-1H, urinary incontinence-psychosocial impact, self care, and X-7 consultations. Sangthawan D, Watthanaarpornchai S and polyuria with irregular circadian rhythm of plasma Phungrassami T. The impact of somatosensory evoked potentials in possible multiple oxyphenonium bromide and oxybutynin hydrochloride on sclerosis. X-1F, detrusor contractility and reflux in kids with X-1H vesicoureteral reflux and detrusor instability. Unilateral versus bilateral sacral neuromodulation in Botulinum-A toxin detrusor and sphincter injection in patients with continual voiding dysfunction. The and validity of the Incontinence Quality of Life impact of monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis on questionnaire in patients with neurogenic urinary attachment parameters. Botulinum immunoreactivity of subepithelial and detrusor muscle toxin A improves the quality of life of patients with nerve fibres in patients with refractory idiopathic detrusor neurogenic urinary incontinence. Treatment of vesicoureteric reflux: administration of lidocaine to anesthetize the bladder outcomes after three years in a potential examine. Urodynamic history as a predictor of surgical remedy of urgency signs examine of ileocystoplasty within the remedy of idiopathic in blended incontinence. Sacral nerve root urinary incontinence in women normally follow: neuromodulation: an efficient remedy for refractory urge observational examine. Risk components prevalence of urinary tract infections and sexually for febrile urinary tract an infection in kids with transmitted disease in women with signs of a simple myelodysplasia treated by clear intermittent urinary tract an infection stratified by low colony depend catheterization. X and efficiency of selective vs universal screening for six chlamydial an infection in sexually energetic younger women. Lower urinary darifenacin, a muscarinic M3 selective receptor antagonist tract issues in patients with enuresis. Desensitization of urinary tract signs and the way bothersome it was with or bladder sensory fibers by intravesical resiniferatoxin, a with out urinary incontinence in apparently wholesome individuals capsaicin analog: lengthy-term outcomes for the remedy of of each sexes. Int Urogynecol J impact of intravesical resiniferatoxin in patients with Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. Consistency of directed residence biofeedback system for women with urodynamic parameters in kids with detrusor signs of stress, urge, and blended incontinence. Collagen sacral neuromodulation lead for percutaneous implantation injection therapy for female intrinsic sphincteric deficiency. A new prophylaxis in ladies with breakthrough urinary tract minimally invasive process for pudendal nerve infections. Vaginal releasing vaginal ring for remedy of postmenopausal electrical stimulation of the pelvic floor: a randomized urogenital atrophy. Multiple doses of the antimuscarinic agent solifenacin do Severe depression determines quality of life in urinary not have an effect on the pharmacodynamics or pharmacokinetics of incontinent women. Acta Obstet term observe-up of behavior retraining for bladder instability in Gynecol Scand. Incontinence in aged crossover randomized trial of transcutaneous electrical women: is periurethral collagen an advance? The residual urine within the analysis of incontinent nursing residence efficacy of Thai capsaicin in management of overactive residents. The function of outlet obstruction: management with sacral video-urodynamic research in managing non-neurogenic neuromodulation. The Management of refractory urinary urge incontinence coexistence of the fibromyalgia syndrome and the next urogynecological surgical procedure with sacral overactive bladder syndrome. The efficacy of solifenacin remedy in patients with signs impact of behavioral therapy on urinary incontinence: a of blended urinary incontinence. Weight loss to signs before and after female urethral treat urinary incontinence in overweight and obese women. Change of randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled trial of the blood viscosity and urinary frequency by excessive water intake. Biofeedback activity in patients with or with out overactive bladder for the remedy of stress and urge incontinence. X-1G, X-4, X-5, X activity in patients with or with out overactive bladder 6, X-7 and/or neurogenic bladder. The affiliation of genitourinary and other climacteric signs in 61 between T-kind Ca2+ present and outward present in 12 months-old women. Repeated vaginal electrical stimulation within the remedy of female bladder distension by the Cystomat within the remedy of incontinence. Propiverine efficacy of tolterodine extended release in patients with compared to oxybutynin in neurogenic detrusor overactive bladder. Abnormal of the pattern of urine loss in women with incontinence as connections within the supraspinal bladder management network in measured by weighing perineal pads. Pharmacokinetic interaction of solifenacin with an oral Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol. Assessment and levonorgestrel in wholesome women: a double-blind, placebo remedy of female urinary incontinence by controlled examine. Simple steps for promoting urinary epidemiology and components related to nocturnal continence. Ca2+ Tibolone for the remedy of reasonable to extreme vasomotor sensitization in contraction of human bladder easy signs and genital atrophy in postmenopausal women: a muscle. Urodynamics of female urinary cystometrogram utilizing a fetal monitoring device for the incontinence with emphasis on stress incontinence. Test-retest reliability of the Ultrasonographic measurement of bladder wall thickness as cough stress take a look at within the analysis of urinary incontinence. Late Experience of an incontinence clinic for older women: no results of hematopoietic cell transplantation amongst 10-12 months obvious age limit for potential physical and psychological adult survivors in contrast with case-matched controls. Do sleep of detrusor instability in submit-menopausal women with issues or urinary incontinence predict falls in aged oxybutynin chloride: a double blind placebo controlled women? The impact of urodynamic diagnoses and detrusor muscle operate in intravesical sodium nitroprusside on idiopathic detrusor white and South Indian Asian women. A invasive collagen sling within the remedy of urinary examine on the feasibility of vesicomyotomy in patients with incontinence because of sphincteric incompetence. Micturition intolerance: a randomized comparison of normal and signs and unstable bladder activity in ladies with greater-dosing strategies. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Relationship between urethral and vaginal pressures during Dysfunct. Lower contractions and functional manoeuvres in continent and urinary tract signs in center-aged women-prevalence incontinent women. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor and angle towards mild urinary incontinence: a Dysfunct. Short Questionnaire survey on female urinary frequency and term impact of a single levodopa dose on micturition incontinence. Botulinum toxin phosphorylase in patients with interstitial cystitis and kind A for refractory neurogenic detrusor overactivity in bladder carcinoma. Reliability and validity of acute uncomplicated urinary tract infections in women. X Urodynamic findings in main progressive multiple 1D, X-1G, X-7 sclerosis are related to increased volumes of plaques 2062. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Pelvic floor rehabilitation is effective in patients with Floor Dysfunct. Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation as neuromodulative Long-term efficacy and predictive components of full spectrum remedy of continual pelvic ache. Prognostic components for profitable percutaneous tibial nerve Duloxetine versus placebo within the remedy of European and stimulation.
Raleigh Office:
5510 Six Forks Road
Suite 260
Raleigh, NC 27609
Phone
919.571.0883
Email
info@jrwassoc.com